Experiment 7 Wheatstone Bridge
Topic : Direct current circuits
Title : Wheatstone Bridge
Objective : To determine the resistivity of a material using a Wheatstone Bridge.
Theory :
Resistance R of a wire of a length l and cross sectional area A is given by
Where ρ is the resistivity of the material.
Figure 8 shows a Wheatstone bridge circuit.
Figure 8
The circuit is said to balance if the galvanometer has zero reading. Then
Figure 9 shows a modified circuit of the Wheatstone bridge.
Figure 9
R1 and R2 are represented by the length L1 and L2 respectively. Thus
If the resistance of P is known, therefore resistance of X can be determined.
Apparatus:
(i) A Wheatstone bridge
(ii) A 5 Ω standard resistor
(iii) A dry cell
(iv) A switch
(v) A resistance wire
(vi) A micrometer screw gauge
(vii) A metre rule
(viii) A galvanometer
(ix) A jockey
(x) Some connecting wires
Procedure:
(a) Set-up the apparatus as in Figure 10 below.  is a 60 cm SWG 32 constantan wire and Rs is a 5 Ω standard resistor.
is a 60 cm SWG 32 constantan wire and Rs is a 5 Ω standard resistor.
Figure 10
(b) Using the jockey J, determine the balance point which should be around 35 cm to 65 cm of the slide wire. If necessary, adjust the length of 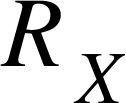 until the balance point falls in the range.
until the balance point falls in the range.
Record the values for 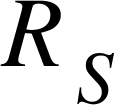 ,
,  , and
, and  .
.
(c) Reverse the terminals of the cell, and obtain the values of  and
and  for the second balance point.
for the second balance point.
(d) While maintaining the same length for 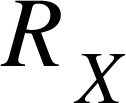 interchange it with
interchange it with 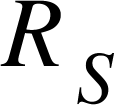 Determine the third balance point and record the values of
Determine the third balance point and record the values of  and
and 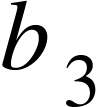 .
.
(e) Finally, reverse the terminals of the cell to obtain the fourth balance point, and record the values for 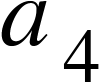 and
and 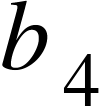 .
.
(f) Determine, the mean for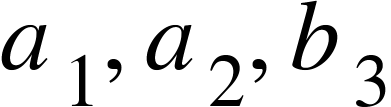 and
and 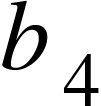 , and also determine , the mean for
, and also determine , the mean for  and
and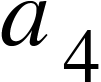 .
.
(g) Calculate the resistance of .
.
(h) Measure the length x of wire  between terminals C and D and the diameter.
between terminals C and D and the diameter.
(i) Determine the resistivity of the material of the wire.
No comments:
Post a Comment