Experiment 1 Introduction To Uncertainty Analysis
Topic : Physical Quantities and Units
Title : Introduction to Error Analysis
Objective : To estimate the accuracy of experimental result
Theory :
Error or uncertainties could be caused by limitation of the measuring instruments, nature of
the measured quantities or other external factors. Error can be classified as systematic error
and random error.
the measured quantities or other external factors. Error can be classified as systematic error
and random error.
Error analysis is a technique used to determine how error propagates through experimental
procedure. This technique is based on combining the uncertainty for each quantity involved
to estimate the accuracy of the experimental result.
procedure. This technique is based on combining the uncertainty for each quantity involved
to estimate the accuracy of the experimental result.
Propagation of errors: Assume A and B are two measured quantities in an experiment.
- Addition or Subtraction
If the derived quantity 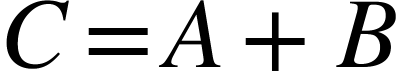 or
or  , then
, then
- Multiplication and Division
If the derived quantity  or
or  , then
, then
The experimental result should be expressed as 
The accuracy of the experimental result can be estimated by calculating the percentage error.
Percentage error 
Apparatus:
(i) A measuring cylinder
(ii) A glass rod
(iii) A triple beam balance
(iv) A micrometre screw gauge
(v) A half-metre ruler
![WP_20180624_14_32_57_Pro[1] WP_20180624_14_32_57_Pro[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj4U1F_QGuWx3AvdK1HZuUCPztN5b8vm9yEEUd691A6S-xPsSSqQi9CAkZ5iJ5ly7SZplFUaCLkyvN-fUwhPzMn3R94lusN_G7Zx7jF-O2UPBVRN3cqtvSvSeEXv2R4D0GMdxYytQy_uEs/?imgmax=800)
Procedure:
Part I: To estimate the error in the determination of density of water.
- Weigh an empty measuring cylinder.
- Measure 200 cm3 of water using the measuring cylinder.
- Weigh the filled measuring cylinder.
- Calculate the density of water.
- Estimate the error in your result.
Part II: To estimate the error in the determination of density of glass.
- Measure the diameter and length of a glass rod.
- Weigh the glass rod.
- Calculate the density of the glass rod.
- Estimate the error in your result.
Data :
![WP_20180624_14_14_49_Pro[1] WP_20180624_14_14_49_Pro[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh4-zGPqqlABmVjOyl4I8rp56nDZ6SJa68UVT2F7m44mYWjVN7MNUKFCy8xUEt-rxbbSic9IB8tbR5mwIbUDXBP3eyYfjokAolNLLVG1LwUJlIZeRSS15tRgzVstC7f7cJZX1i5yTkh7r0/?imgmax=800)
![WP_20180624_14_15_35_Pro[1] WP_20180624_14_15_35_Pro[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjYvQawAfwxLKyIIZVVZoG3QdUBhN5pgGeXzldCV6DDIatJax1_TLjPufxe7Vh1eHsOAFhDl2JaDHKHyV9e8TAXY4URJyxhh2rCZEtP4EqEIhITI_G7pRV9NNRGIXadB-gYrDo6kXfCUOE/?imgmax=800)
![WP_20180624_14_14_04_Pro[1] WP_20180624_14_14_04_Pro[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgoJqorFNy9PWHR4wxv10UBn7n1YlFhIZ4KbEWD2T0YAFOfLbScbrLRbi5zunUFiD6uolY6VV9WbsFsbV0cIqUsKCBBCZ_tEO03arcTIQdXFlDX2TXAxhk4DWZLaElTO-vxpT4BlxAevJo/?imgmax=800)
![WP_20180624_14_12_48_Pro[1] WP_20180624_14_12_48_Pro[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjDQzxS-AgnhDTIEa0o4PKjnWNj7AYM30Y7xmVu9e-sIw8ImlBnZpN0Y4kE-JpE1LnTFhZf0bj-Q3vnJ97WKA4ZhduH0wWC9sokQJN3UCUyBNRNCtmhbT43nYYfXnEugcCkl5qEx-LypzQ/?imgmax=800)


No comments:
Post a Comment